What Is Regional Anesthesia?
Regional anesthesia is a way to block pain in a specific part of your body. Doctors use it during surgeries or procedures. Instead of putting you to sleep, they numb only the area that needs treatment. For example, you may get a nerve block in your arm or leg. This method helps you stay awake and recover faster. However, like any medical procedure, it can have some risks.
What Are Regional Anesthesia Complications?
Regional anesthesia complications are problems that can happen after the procedure. Most people do not have any issues. Yet, some may experience side effects. These can include:
Although most side effects are mild, some, like hematoma after nerve block, need quick attention.
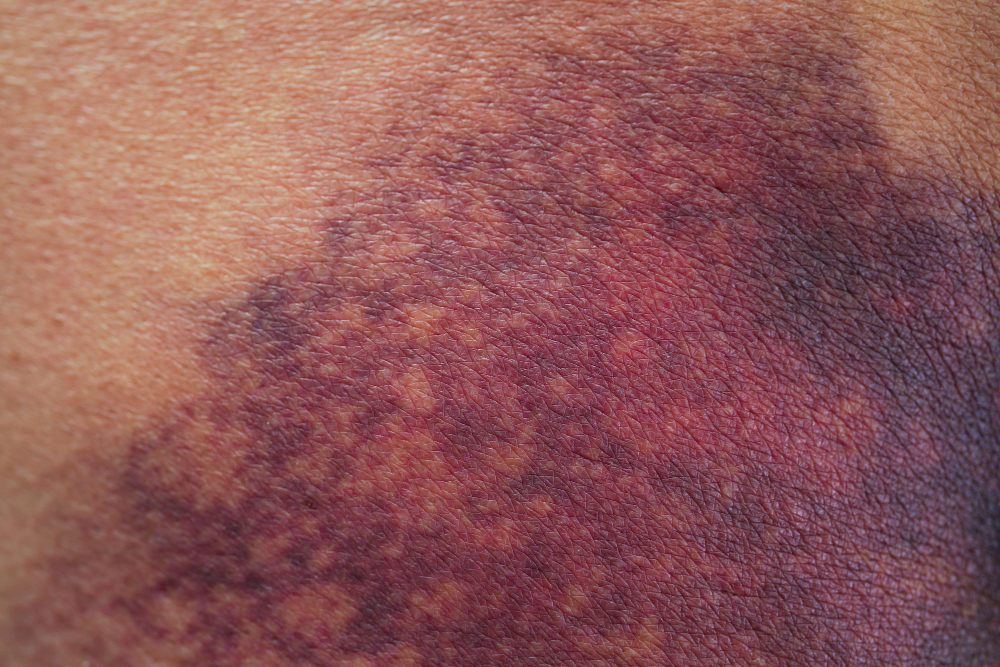
What Is Hematoma Formation After Regional Blocks?
A hematoma is a collection of blood outside a blood vessel. After a regional block, bleeding can occur under the skin or in deeper tissues. This blood can pool and form a lump. While small bruises are common, a large hematoma can press on nerves or other tissues. This may cause pain or other problems. Hematoma after nerve block is rare, but it is a known regional anesthesia complication.
Symptoms and Warning Signs of Hematoma
It is important to know the signs of a hematoma. Early detection helps prevent serious issues. Watch for these symptoms:
If you notice any of these warning signs, contact your doctor right away. Quick action can prevent further problems.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several things can increase the risk of hematoma formation after regional blocks. Some common causes and risk factors include:
Knowing these risks can help you and your doctor take steps to prevent problems.
Diagnosis and When to Seek Help
If you have symptoms of a hematoma after nerve block, see a healthcare provider soon. They may:
Early diagnosis is key. If you have severe pain, numbness, or trouble moving the limb, seek emergency care. These could be signs of nerve pressure or other serious complications.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the size and location of the hematoma. For small hematomas, doctors may suggest:
For larger hematomas or those causing nerve problems, you may need further treatment. Sometimes, doctors drain the blood or perform surgery. Your care team will choose the safest option for you.
Prevention Tips and Lifestyle Guidance
There are steps you can take to lower your risk of hematoma during anesthesia:
By staying informed and prepared, you can help prevent hematoma after nerve block and other regional anesthesia complications.
Conclusion
Regional anesthesia is safe for most people, but complications like hematoma can happen. Knowing the signs, causes, and prevention tips helps you stay safe. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice on regional anesthesia complications.